Have you ever sat down at a restaurant, asked for olive oil, and wondered if what you got was the real thing or fake olive oil?
I used to trust what arrived at the table. Then my grandson was diagnosed with a soybean oil allergy, and I became a detective, mapping Portland-area restaurants where he could eat safely.
The results were not encouraging. Many kitchens relied on soybean oil, even in dishes that should use olive oil. One Italian chain admitted they dilute their olive oil with soybean oil. Another pasta place said they could use olive oil only by request. A chef told me, “If you have an allergy, I wouldn’t trust my staff not to grab the wrong oil.”
That search was years ago, but it taught me to pay attention. Fast forward a decade or so. I’d been dealing with my own reactions to restaurant food for years—regardless of what I ordered. I finally figured out I was reacting to soybean oil and any oil that had been overheated. Recently, I ordered a salad with olive oil, took one look, and passed. It was thin, pale yellow, odorless, and tasted greasy, so I knew it wasn’t real.
If restaurants are cutting corners on olive oil, what does that mean for your health?
Why Olive Oil Quality Matters for Your Brain, Heart, and Bones
Olive oil isn’t just a cooking fat. Its medicinal value is remarkable.
Brain Health: Protection Against Dementia
A 2024 Harvard study following over 92,000 adults for 28 years found something remarkable: people who consumed more than 7 grams of olive oil daily (about half a tablespoon) had a 28% lower risk of dying from dementia compared with those who never or rarely consumed olive oil. Even more striking, this benefit held regardless of overall diet quality.
The researchers also found that replacing just one teaspoon of margarine or mayonnaise with olive oil was associated with an 8% to 14% lower risk of dementia-related death.
The brain-protective effects come from olive oil’s high content of monounsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols. These compounds have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may protect neurons from damage and support cognitive function as we age.
Bone Health: Stronger Bones, Fewer Fractures
Olive oil’s benefits for bone health are equally impressive and often overlooked.
Research following 870 participants for nearly 9 years found that people consuming the highest amounts of extra virgin olive oil had a 51% lower risk of osteoporosis-related fractures compared to those consuming the least. Common olive oil showed no such benefit, highlighting the importance of polyphenol compounds found only in the highest-quality oil.
Olive oil protect bones in several ways, including:
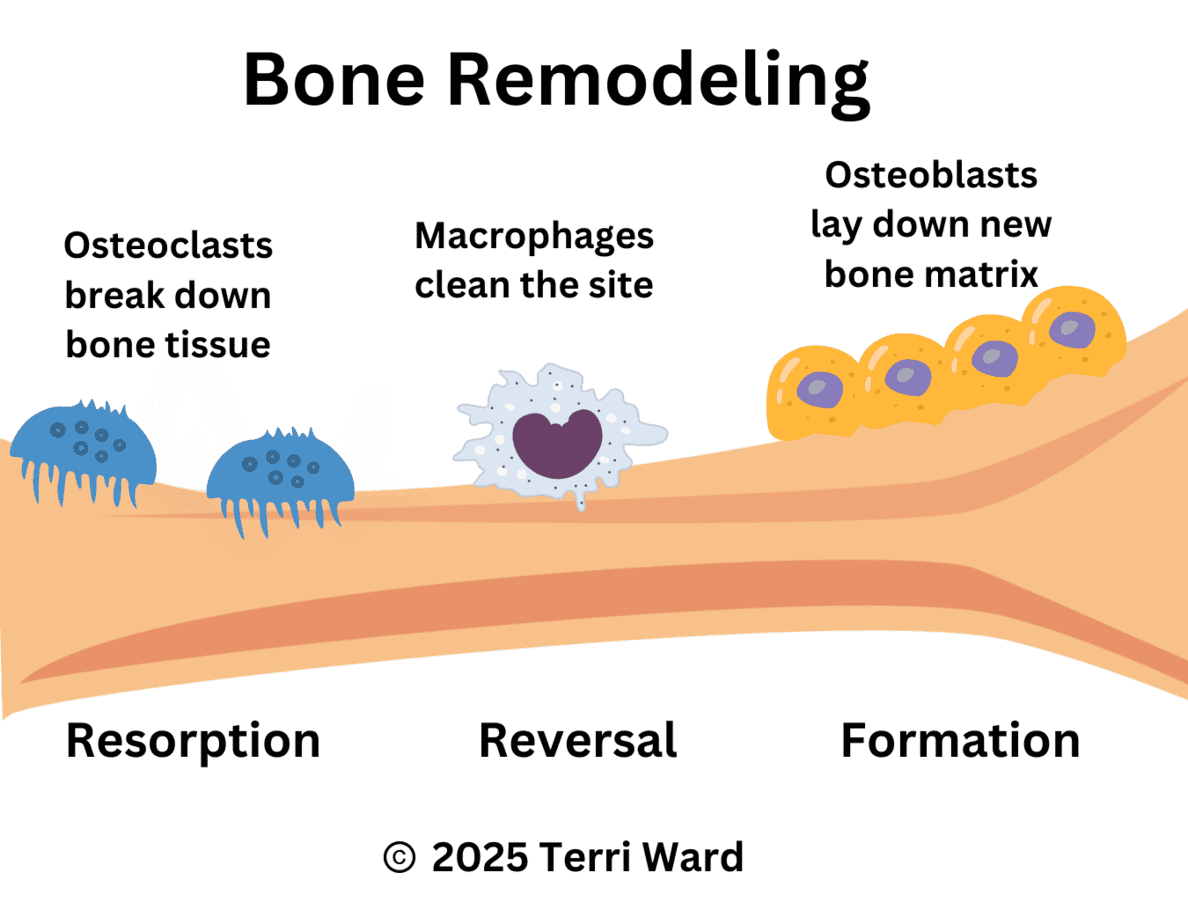
Reducing inflammation – Chronic inflammation disrupts the balance between osteoclasts (cells that break down bone) and osteoblasts (cells that build new bone). When inflammation runs high, bones break down faster than they rebuild. Olive oil’s polyphenols, particularly oleuropein, calm this inflammatory response and help maintain healthy bone remodeling.
Increasing osteocalcin – This is a key protein produced by osteoblasts that helps mineralize bone tissue. Studies in postmenopausal women with osteopenia (low bone density) showed that consuming olive polyphenol extract for 12 months significantly increased osteocalcin levels and stabilized bone mineral density in the lumbar spine, while the placebo group continued losing bone mass.
Supporting calcium metabolism – Olive oil enhances the body’s ability to utilize calcium effectively, improving bone mineralization and strength.
Heart Health and Beyond
Olive oil’s cardiovascular benefits are well established. Multiple large reviews and cohort studies show that higher olive-oil intake is linked to fewer major cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke, and to lower risks of coronary heart disease and peripheral artery disease. Olive-oil intake is also associated with a lower risk of death from cardiovascular disease and from any cause.
How does it work? Extra-virgin olive oil favors a healthier lipid profile by lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, improving blood vessel function, and reducing inflammation throughout the circulatory system. The same polyphenols that support brain and bone health also protect your heart and blood vessels.
Olive oil’s health benefits are remarkable, but only if the olive oil is unadulterated..
The Problem of Fake Olive Oil Is Real and Growing
Fake olive oil isn’t new, but the problem is getting worse as drought and crop failures drive prices up. When half-liter bottles sell for $20 to $70, some sellers dilute real olive oil with cheap seed or refined olive oils, tint it with chlorophyll and beta-carotene, and sell it at premium prices.
In 2024 and early 2025, authorities across Europe exposed large operations: Portuguese officials seized 16,000+ liters of mislabeled oil, and Italian police cracked a ring blending low-grade oils with chemicals.
Fortunately, recent FDA testing of 88 U.S. retail samples found low adulteration rates among major brands. Risk rises with no-name or ultra-cheap brands, restaurant oils, or labels missing a harvest date or clear origin.
The studies showing 51% lower fracture risk and 28% lower dementia risk were done with authentic extra-virgin olive oil—not adulterated blends. Counterfeit oils can promote inflammation and introduce allergens that trigger reactions in sensitive individuals (like my grandson). Thus, choosing pure olive oil is essential.
How to Identify Real Olive Oil
Here’s what I’ve learned to look for and avoid buying olive oil:
Dark glass or tin – Light degrades oil, so avoid clear containers as well as plastics. Most restaurants buy olive oil in metal tins because they’re durable and light-proof, but those
containers are lined with undisclosed coatings. For home use, I recommend dark glass and smaller bottles to maintain freshness.
Harvest date – Look for an actual harvest date, not just a “best by” date. Aim to use it within 18 to 24 months of harvest. No harvest date is a red flag.
“Extra virgin” designation – This is the highest grade, meaning it was extracted without heat or chemicals. Still verify the other cues below.
Cold-Pressed Matters – Real extra-virgin olive oil is mechanically extracted without heat or solvents, preserving its fragile polyphenols. Refined or “light” olive oils are processed with high heat or chemicals, destroying those protective compounds and sometimes masking lower-quality oil.
Specific origin – Look for where the olives were grown and pressed, not vague “Product of Italy” wording.
Price that makes sense – If it seems too cheap to be true, it probably is. Quality extra-virgin olive oil costs more because production is labor-intensive.
Trust your senses:
- Color: Real extra virgin olive oil ranges from deep green to golden yellow, never pale or clear.
- Aroma: It should smell fresh, fruity, and sometimes grassy or peppery, never musty or bland.
- Taste: Quality olive oil has a distinct flavor with slight bitterness or pepperiness. If it tastes bland or greasy, it’s likely diluted or low-grade.
Want a quick-reference guide?
Download my free chart: “How to Tell Real vs. Fake Olive Oil”—perfect for printing or saving to your phone next time you shop.
How to Avoid Fake Olive Oil at Restaurants
A few restaurants now avoid seed oils thanks to growing consumer demand (you can find them in the Seed Oil Scout app). When dining out elsewhere, here’s what you can do:
- Choose restaurants that prioritize quality ingredients and are transparent about their practices.
- Ask specifically if the olive oil is 100% olive oil or if it’s blended.
- Bring your own olive oil for salad dressings if you’re highly sensitive.
- Clearly communicate any allergies to the wait staff, and ask to speak with the manager if needed.
Restaurants operate on thin margins, and olive oil is expensive. Dilution saves them money, but it can cost you the health benefits you’re expecting.
Cooking with Real Olive Oil
Low heat cooking is often recommended, but with a smoke point ranging from 350°F to 410°F, it’s suitable for sautéing, baking, and roasting, as well as salad dressings and finishing dishes. The key is not to overheat it. For higher-heat cooking like deep frying, choose a fat with a higher smoke point like avocado oil or beef tallow.
Olive Oil in God’s Design
Olive oil appears throughout Scripture—not as a luxury, but as a staple of provision, healing, and abundance.
In ancient times, olive oil was used for anointing kings (1 Samuel 16:13) and priests (Exodus 30:22–33), for lighting sacred lamps (Exodus 27:20), and for treating wounds (Luke 10:34, James 5:14). The oil itself was so valuable that it represented God’s blessing and favor (Psalm 23:5, Jeremiah 31:12). The olive tree, which can live for thousands of years and continues producing even in harsh conditions, symbolizes endurance and faithfulness (Psalm 52:8, Romans 11:17–24, Genesis 8:11).
There’s something profound about a food so central to biblical life also being one of the most scientifically validated for human health. The same oil used to anoint David as king is now shown to protect against dementia and fractures. God’s design has always been intentional. He packed olive oil with compounds our bodies desperately need, long before science could explain why.
This isn’t coincidence. It’s provision (Deuteronomy 6:10–11, 1 Kings 17:12–16).
The Bottom Line
What started as detective work for my grandson’s allergy opened my eyes to a much bigger issue: we can’t always trust what we’re told we’re eating. But unlike so many aspects of our health that feel out of our control, this one isn’t.
You have the power to choose pure versus adulterated olive oil, to ask the right questions, to protect your brain, strengthen your bones, and nourish your body the way God intended.
The science is clear: genuine extra virgin olive oil offers remarkable protection. The fraud is real, but so are the solutions.
Your health—and your family’s health—is worth being discerning. It’s worth paying attention to harvest dates and dark bottles. It’s worth the slightly higher cost and the extra effort.
Because when you choose real food, you’re choosing a longer, healthier life. And that’s a choice worth making.
Looking for more ways to support your health?
- Explore the recipes on this site that use pure, nutrient-dense foods.
- Read The Dangers of Seed Oils and Trans Fats in my Anti-Inflammatory Rainbow Diet™
- Discover evidence-based guidance in my book God’s Prescription: A Faith-Based Plan to Shift Your Mindset and Reclaim Your Natural Health.
- Don’t forget your free quick-reference guide.
References
Brain Health:
- Tessier AJ, et al. Consumption of olive oil and diet quality and risk of dementia-related death. JAMA Network Open. 2024;7(5):e2410021. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2818362
- National Institute on Aging. Olive oil consumption linked with lower risk of dementia-related death. Published May 2024. https://www.nia.nih.gov/news/olive-oil-consumption-linked-lower-risk-dementia-related-death
Bone Health:
- García-Martínez O, et al. Extra virgin olive oil consumption reduces the risk of osteoporotic fractures in the PREDIMED trial. Clinical Nutrition. 2018;37(1):329-335. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28143667/
- El-Shafaey E, et al. Is extra virgin olive oil a promising remedy for reducing the impact of postmenopausal osteoporosis? An experimental study. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2025;12:1555779. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40125318/
- Santiago-Mora R, et al. Twelve-month consumption of a polyphenol extract from olive (Olea europaea) in a double blind, randomized trial increases serum total osteocalcin levels and improves serum lipid profiles in postmenopausal women with osteopenia. Journal of Nutrition Health and Aging. 2015;19(1):77-86. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1279770723014355?via%3Dihub
- Chin KY, Ima-Nirwana S. Olives and bone: International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016;13(8):755. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/13/8/755
- Fernández-Real JM, Bulló M, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ricart W, Ros E, Estruch R, Salas-Salvadó J. A Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil is associated with higher serum total osteocalcin levels in elderly men at high cardiovascular risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Oct;97(10):3792-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2221. Epub 2012 Aug 1. PMID: 22855341; PMCID: PMC3462931. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22855341/
Fraud and Adulteration:
- European Union Food Fraud Network. 2024-2025 fraud investigations and annual reports. https://food.ec.europa.eu/document/download/a47b9d6a-9b47-4b57-a1ca-35e5bbfa837f_en?filename=acn_annual-report_2024.pdf
- S. Food & Drug Administration. Olive oil authenticity testing results. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society. 2015. · https://aocs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1007/s11746-015-2759-4
FDA summary: https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/fda
- Food Navigator. Olive oil a major target for food fraud. Published May 8, 2025. https://www.foodnavigator.com/Article/2025/05/08/olive-oil-a-major-target-for-food-fraud/
Cardiovascular Health:
- Katsiki N, Pérez-Martínez P, Lopez-Miranda J. Olive Oil Intake and Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: “Seek and You Shall Find”. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021 May 7;23(6):64. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01496-1. PMID: 33961163. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33961163/
- Guasch-Ferré M, et al. Olive oil intake and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in the PREDIMED Study. BMC Medicine. 2014;12:78. https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1741-7015-12-78
- Estruch R, et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts. New England Journal of Medicine. 2018;378(25):e34. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30285333/
Olive Oil’s Smoke Point:
- Michigan State University Extension. Olive oil 101. https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/olive_oil_101. Published March 12, 2015. Accessed October 29, 2025.
- Arkansas Cooperative Extension Service. Olive Oil. https://www.uaex.uada.edu/life-skills-wellness/extension-homemakers/03%20OliveOil%20H2.pdf. Accessed October 29, 2025.
- UC Davis Olive Center. Ten Myths and Facts About Olive Oil. https://olivecenter.ucdavis.edu/sites/g/files/dgvnsk14776/files/media/documents/myths1933.pdf. Accessed October 29, 2025.